As the application of metal 3D printing becomes more and more popular, many companies use the metal 3D printing process to customize production samples in the early stage of product development; however, due to the lack of understanding of the metal 3D printing process, many mistakes often occur, the metal printed samples failed to meet the expected ideal requirements, so we have summarized the most common questions and answers!
What are the precautions for designing 3D printed metal parts?
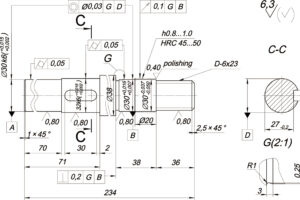
- Tapping is recommended for the thread, and direct printing (including internal and external threads) is not recommended.
- Wall thickness, slot width, and font size below 0.5mm sometimes cannot be printed.
- The assembly parts need to be reminded to send the assembly drawing, and they will be assembled before they are sent out.
- The product gap to be assembled needs to be placed 0.15mm on one side.
- For those with high local assembly requirements (such as bearing hole/diameter/plane assembly position), a machining allowance should be reserved in advance, and then matched by secondary finishing.
- Metal 3D printing is somewhat slender after high-temperature sintering, thin-walled parts, shells and other structures will be deformed. The advantage of metal 3D printing lies in the complex structure, and the precision and surface effect is inferior to machining.
- Natural surface pitting (about Ra7).
- Post-processing of metal 3D printing materials: Like traditional materials, they can be processed for subsequent secondary processing.
- The printing tolerance of products within 9.50mm is ±0.1mm, and the printing tolerance of larger products depends on the paper.
- For large-sized products, if you need to disassemble and print, you must consider the disassembly position, avoid the hole position, consider the amount of deformation and reserve the alignment interface during welding.
Many of the above precautions need to be optimized and improved from the design of 3D drawings. To shorten the period of the sample and reduce the probability of printing failure, it is recommended that you consider the above factors when drawing.
What are the common metal 3D printing materials and their advantages?
- Material advantages of titanium alloy (TC4): high strength and low density, good mechanical properties, good toughness and corrosion resistance, lightweight and good biocompatibility.
- Material advantages of aluminum alloy (AlSi10Mg): high plasticity, high corrosion resistance, good electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity, and ease to withstand various pressure processing and stretching, bending, gas welding, argon arc welding, and spot welding, The technology is mature, the quality is stable, the material structure is uniform, and the density is small.
- Material advantages of stainless steel (316L): high strength, corrosion resistance, good heat resistance, and excellent polishing performance.
- Material advantages of die steel (1.2709 and CX): high toughness and good heat resistance.
What are the uses of metal 3D printing products?
- Stainless steel and aluminum alloys are most commonly used in industrial fields.
- Die steel is most commonly used for conformal waterways in injection molds.
- Titanium alloys are commonly used in the military, aerospace, and medical industries.