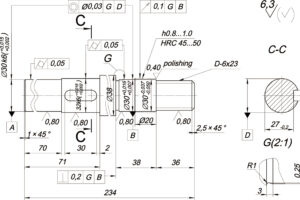
Blackening is a common method of chemical surface treatment, a method of steel surface treatment. The function is to use the chemical reaction method to form a tight protective film on the steel parts to prevent the spring sheet from being corroded.
There are two ways of blackening, Black Oxide treatment and phosphating treatment. The two blackening treatments have low cost and high production efficiency. We detail the differences between these two processes in this article.
What is Black Oxide?
All metals are covered with an oxide film in the air. However, under natural conditions, the oxide film formed on the metal surface due to corrosion is sometimes very thin, often loose and uneven, and cannot effectively protect the metal from continued corrosion and damage. Therefore, it is necessary to use artificial methods to treat the metal surface to form a thick, uniform, stable, tight, and protective oxide film firmly bonded to the substrate. This surface treatment process is called oxidation. The oxidation treatment of steel and its alloys is also called bluing or blackening treatment due to forming a blue or black oxide film on the surface. The appearance and performance of the obtained oxide film depend on the metal composition, surface state and oxidation treatment process. The thickness of the film layer is about 0.6 to 1.5 μm. Therefore, the oxidation treatment does not affect the accuracy of the workpiece product itself. Oxidation treatment of steel is often used for protection, decoration or other purposes of workpieces such as machinery, instrumentation, weapons and daily necessities.
There are two commonly used methods for blackening treatment: the traditional alkaline heating blackening and the late-appearing typical temperature blackening. However, the blackening process at room temperature is ineffective for low carbon steel. Alkaline blackening of A3 steel is better.
At high temperatures (about 550 ℃), the ferric oxide formed by oxidation is sky blue, which is called bluing treatment. Ferric oxide formed at low temperature (about 350°C) is dark black, which is called blackening treatment. In weapon manufacturing, bluing treatment is commonly used; blackening treatment is widely used in industrial production.
What is the phosphating process?
Phosphating is putting the metal workpiece into some metal phosphate solution for treatment so that a protective film formed by insoluble phosphate, a phosphating film, is formed on the surface of the workpiece.
Phosphate film has specific anti-corrosion properties. Under normal atmospheric conditions, the phosphating film has high stability in lubricating and anti-rust oil. It has good adhesion performance and porosity structure, so lubricating oil such as anti-rust oil can be well adsorbed on its surface and lubricate the workpiece well. It is precisely because the phosphating film has many pores. It cannot effectively prevent corrosion for a long time, especially when it encounters acids and alkalis; the phosphating film is easily damaged. Therefore, after phosphating, the workpiece generally needs to be immersed in anti-rust oil for supplementary anti-rust treatment. After soaking in phosphating anti-rust oil, the anti-rust oil can form a dense anti-rust oil film on the surface of the workpiece, thus significantly improving the corrosion resistance of the phosphating workpiece.
In addition, the phosphating workpiece, because of the soft phosphating film, is also used to reduce the friction during metal pressure processing, wire drawing, etc., improve the running-in property of partner parts, and improve the wear resistance of the workpiece. For example, the electrically insulating layer of the transformer silicon steel sheet, the motor rotor or the stator silicon steel sheet using phosphating treatment in the electrical industry has a high resistance, and the withstand voltage can reach 1KV. The molten metal cannot be attached to the phosphating film, which can be used as a protection for individual parts when the bushing and bearing are cast; phosphating after nitriding can improve the hardness of the nitriding layer.
The phosphating liquid is essential in the phosphating process; the phosphating liquid used in different phosphating will be extra. After the metal workpiece is put into the phosphating solution, a chemical reaction occurs with each other to generate an iron phosphate element, and hydrogen and oxygen are also developed. This iron carbonate element will slowly crystallize and deposit on the metal surface. When more and more crystals are formed, they will join together on the metal surface to form a layer of water-insoluble and firm phosphating film.
After the workpiece is put into the phosphating solution, it needs to be shaken continuously for a few minutes, mainly to discharge the air and air bubbles trapped in the groove of the workpiece; the phosphating time is generally determined according to different workpiece structures, materials and temperatures, usually The whole process takes about 30 minutes.
The role of phosphating before painting:
- Enhance the bonding force between the coating film (such as paint coating) and the workpiece.
- Improve the corrosion resistance of the surface coating of the workpiece after painting.
- Enhance the beauty of the parts.
The role of non-coating phosphating: improve the wear resistance of the workpiece so that the workpiece has lubricity in the machining process; after proper post-treatment, the wear resistance of the workpiece can be improved.
Phosphating application: Phosphating film is mainly used as the bottom layer of paint, lubricating layer during cold working, metal surface protective layer, insulation treatment of motor silicon steel sheet, anti-stick treatment of die-casting mold, etc. It is widely used in industrial production such as automobiles, ships, aerospace, machinery manufacturing and home appliances.