What is die casting?
Die casting is a metal casting process characterized by using a mold cavity to apply high pressure to molten metal. Molds are usually machined from stronger alloys, similar to injection molding. Most die castings are free of iron, such as zinc, copper, aluminum, magnesium, lead, tin, and lead-tin alloys and their alloys. Depending on the type of die casting, a cold chamber die casting machine, or a hot chamber die casting machine is required.
hot chamber die casting
Its metal pool is a molten state of liquid, semi-liquid metal that fills the mold under pressure. At the beginning of the work, the machine’s piston is in a retracted state, and the molten metal can fill the gooseneck. A pneumatic or hydraulic piston squeezes the metal and plugs it into a die.
The advantages of this system include high cycle speed (about 15 cycles per minute), ease of automation, and ease of melting the metal.
Disadvantages include the inability to die-cast metals with higher melting points and the failure to die-cast aluminum because aluminum would carry iron out of the molten pool. Thus, hot chamber die casting machines are generally used for zinc, tin, and lead alloys. Moreover, hot chamber die casting is challenging for large castings, which are usually die casting of small castings.
cold chamber die casting
The metal needs to be melted first in a separate crucible in this process. A quantity of molten metal is then transferred to an unheated injection chamber or nozzle. These metals are injected into the mold by hydraulic or mechanical pressure. The most significant disadvantage of this process is the long cycle time due to the need to transfer the molten metal into the cold chamber.
Cold chamber die-casting machines are also divided into vertical and horizontal types. Vertical die-casting machines are usually small, while horizontal die-casting machines have various models.
Process steps of die casting
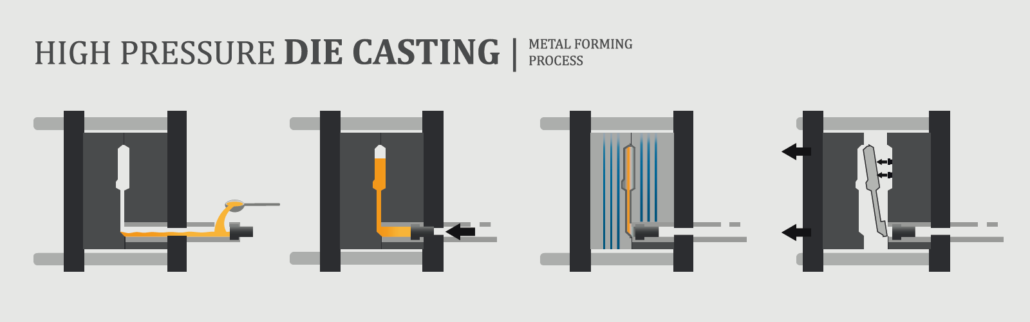
The traditional die casting process mainly consists of four steps, or high pressure die casting. These four steps include mold preparation, filling, injection, and shakeout.
- It is necessary to spray lubricant into the mold cavity in the preparation process. In addition to helping to control the temperature of the mold, the lubricant can also help the casting release.
- Close the mold and inject molten metal into the mold with high pressure, which ranges from 10 to 175 MPa.
- Molten metal filling. The pressure in the mold will be maintained until the casting solidifies.
- The push rod pushes out all castings. Since there may be multiple cavities within a mold, multiple castings may be produced during each casting. The process of falling sand requires the separation of residues, including mold openings, runners, gates, and flash.
Material Options for Die Casting
The minimum cross-sectional area and the minimum draft angle corresponding to various materials are listed in the following table, and the thickest section should be less than 13 mm.
Metal | Minimum cross-sectional area | Minimum draft angle |
Aluminum alloy | 0.89 mm (0.035 in) | 1:100 (0.6°) |
Brass and Bronze | 1.27 mm (0.050 in) | 1:80 (0.7°) |
magnesium alloy | 1.27 mm (0.050 in) | 1:100 (0.6°) |
Zinc alloy | 0.63 mm (0.025 in) | 1:200 (0.3°) |
The characteristics of various metals during die casting are as follows:
- Zinc: The most accessible metal to die-cast, it is economical to manufacture small parts, easy to coat, has high compressive strength, high plasticity, and long-lasting life.
- Aluminum: Lightweight, high dimensional stability when manufacturing complex and thin-walled castings, strong corrosion resistance, good mechanical properties, high thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity, and still high strength at high temperatures.
- Magnesium: easy for machining, high strength-to-weight ratio, the lightest among commonly used die-casting metals.
- Copper: High hardness, strong corrosion resistance, the best mechanical properties of widely used die-casting metals, wear resistance, and strength close to steel.
- Lead and tin: high density, extremely high dimensional accuracy, can be used as particular anti-corrosion parts. Due to public health concerns, this alloy cannot be used in food processing or storage equipment. Alloys of lead, tin and antimony (sometimes with a bit of copper) can be used to make hand lettering and bronzing in letterpress printing.
The upper mass limits for die casting using aluminum, copper, magnesium and zinc are 70 lbs (32 kg), 10 lbs (4.5 kg), 44 lbs (20 kg) and 75 lbs (34 kg), respectively.

Advantages of die casting
- Castings have excellent dimensional accuracy. Usually, this depends on the casting material; typical values are 0.1mm error at the initial 2.5cm dimension and 0.002mm error for each additional 1cm.
- Compared with other casting processes, its casting surface is smooth, and the fillet radius is about 1-2.5 microns.
- It can directly cast internal structures, such as wire sleeves, heating elements, and high-strength bearing surfaces.
- High production efficiency. Our die-casting molds usually have a service life of 60,000 to 80,000 times, while the horizontal cold chamber die-casting machine can die-cast 600-700 times in eight hours, and the small hot-chamber die-casting machine can die-cast 3,000 to 7,000 times in an average of eight hours. (Keyanng 2021 Annual Statistics )
- The utilization rate of materials is high. Due to the characteristics of the die-casting process, the utilization rate of materials is about 60% to 80%, which also reduces the price and cost of die-casting parts (mass production)
Disadvantages of die casting
- High cost. The up-front investment in the design and manufacture of molds and mold-related components is expensive than other machining processes. Therefore, it is more economical to produce many products when manufacturing die castings.
- The die casting process is only suitable for metals with high fluidity, and the casting mass must be between 30 grams and 10 kilograms.
- In regular die casting, the last batch of castings will always have porosity and cannot be subjected to heat treatment or welding. Therefore, in the die-casting products that require secondary treatment, the last batch of castings will be wasted due to unqualified ones.
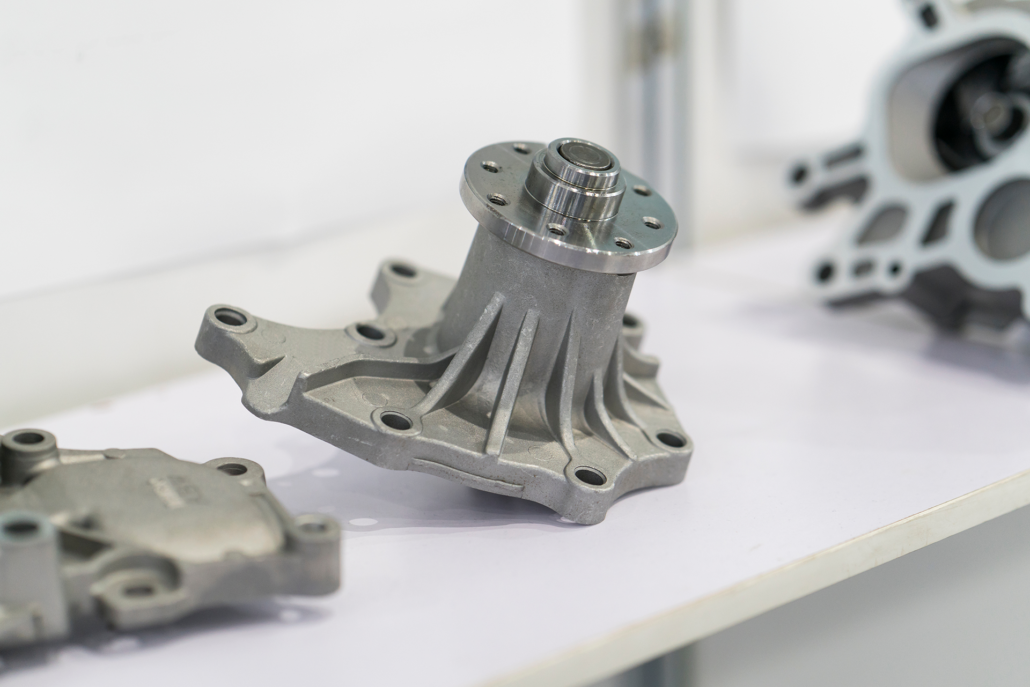
Die Casting Applications
Production of parts and components for automobiles, motorcycles, aerospace products, electrical appliances, instruments, radio communications, computers, agricultural machinery, medical equipment, household appliances, clocks, cameras, architectural decoration, and daily hardware. .
Die-casting parts come in a variety of shapes and can be roughly divided into six categories:
- Disc type, such as number plate holder, etc.
- Round covers, such as watch covers, machine covers, chassis, etc.
- Rings, such as connectors, bearing retainers, steering wheels, etc.
- Cylinders, such as flange jackets, conduits, shell-shaped casings, upper covers, instrument covers, deep cavity instrument covers, camera casings and covers, carburettors, etc.
- Porous cylinder blocks and casings, such as complex castings such as cylinder blocks and cylinder heads of oil pump blocks, and cylinder blocks and cylinder heads of automobiles and motorcycles.
- Special shapes, such as impellers, horns, fonts and other decorative die castings composed of ribs.
Keyanng Die Casting Service
Die casting is a vital sheet metal fabrication process known for its low-cost production and efficiency. And by choosing to manufacture your item in China, you will get a very competitive price.
We are an ISO 9001:2015 certified company with numerous manufacturing plants and state-of-the-art facilities to manufacture high-quality parts. Our delivery time is fast; after uploading your design files, you will get a quote within 12 hours. Contact us for a free quote.