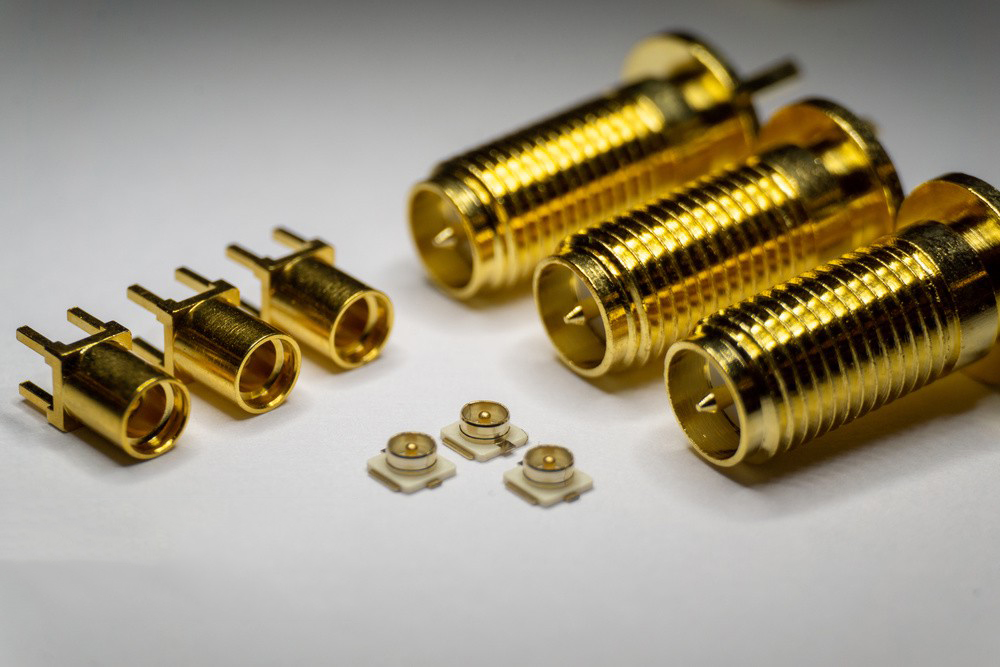
Anodizing is one of the methods of metal surface treatment. Most metal materials (such as stainless steel, zinc alloy, aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy, copper alloy, titanium alloy) can be anodized in a suitable electrolyte.
Electroplating is one of the surface treatment methods for metals and non-metals; as long as they undergo reasonable pretreatment, various metal substrates and some non-metallic materials can be electroplated (for example, ordinary leaves can also be electroplated).
As a product designer, you may need to understand the limitations of different processes so that I will focus on the front:
- The surface treatment of aluminum alloy is usually anodized, which is unsuitable for electroplating.
- The standard surface treatment of zinc alloy die casting is electroplating, which is unsuitable for anodizing.
- Aluminum alloy dies castings are also unsuitable for anodizing, and those with high appearance requirements should be used cautiously.
Usually, the surface treatment of metal alloys is electroplating or anodizing. What is the difference between these two processes?
- Different processing techniques
Electroplating is to use the material to be plated as the cathode, the same metal material as the coating metal as the anode (some insoluble anode is also used), and the electrolyte is a solution containing the metal ions of the coating; a specific current is an input between the anode and the cathode. The coating material and the material to be electroplated are two different materials: beryllium copper nickel plating, beryllium copper as the base material, and nickel as the plating layer.
Anodizing uses chemical or electrochemical treatment to form a film layer containing the metal component on the metal surface. The material to be treated is used as an anode and is protected by a material that forms a film layer on its surface through an external current in a specific electrolyte. If the aluminum alloy is oxidized, a layer of aluminum oxide film is formed on the surface of the aluminum alloy. The aluminum oxide is chemically stable, will not be corrupted again, will not be corroded by acid, and can be dyed in various colours.

- The processed materials are different
The objects processed by the electroplating method are mainly metals but also non-metals. The most commonly used electroplating metals are nickel, chromium, tin, copper, silver and gold. That is to say, nickel-plated, chrome-plated, gold-plated and so on.
Anodizing is a method of metal surface treatment. Most metal materials (such as stainless steel, zinc, aluminium, magnesium, copper, and titanium alloy) can be anodized in a suitable electrolyte.
- The working principle is different
Electroplating is the electroplating material as the cathode, and anodizing is the material to be treated as the anode.
Electroplating is due to the charge effect; the metal anode ions move to the cathode, get electrons at the cathode, and deposit on the material to be plated. At the same time, the metal of the anode dissolves, and the metal ions in the electrolyte are continuously replenished. The electroplating principle includes four aspects: electroplating solution, electroplating reaction, electrode and reaction code, and metal electrodeposition process.
Anodizing is the use of aluminum alloy’s easy oxidation characteristics to control the formation of the oxide layer by electrochemical method to prevent further oxidation of aluminum material and increase the mechanical properties of the surface. In this process, aluminum or aluminum alloy is used as an anode, a lead plate is selected as cathode, and aluminum and lead plate are placed in an aqueous solution containing sulfuric acid and chromic acid, etc. Electrolysis is then carried out to form an oxide film on the surface of the aluminum and lead plates. Of these acids, the most widespread is anodizing with sulfuric acid.
Aluminum alloy anodizing technology is currently the most widely used and most successful. Aluminum alloy anodizing can significantly improve surface hardness and wear resistance.
There are a lot of micropores in the thin oxide film layer, which can adsorb various lubricants, suitable for manufacturing engine cylinders or other wear-resistant parts; the film micropores have strong adsorption capacity and can be coloured into multiple beautiful and bright colours. Non-ferrous metals or their alloys (such as aluminum, magnesium, etc.) can be anodized. This method is widely used in mechanical parts, aircraft and auto parts, precision instruments and radio equipment, daily necessities and architectural decoration.
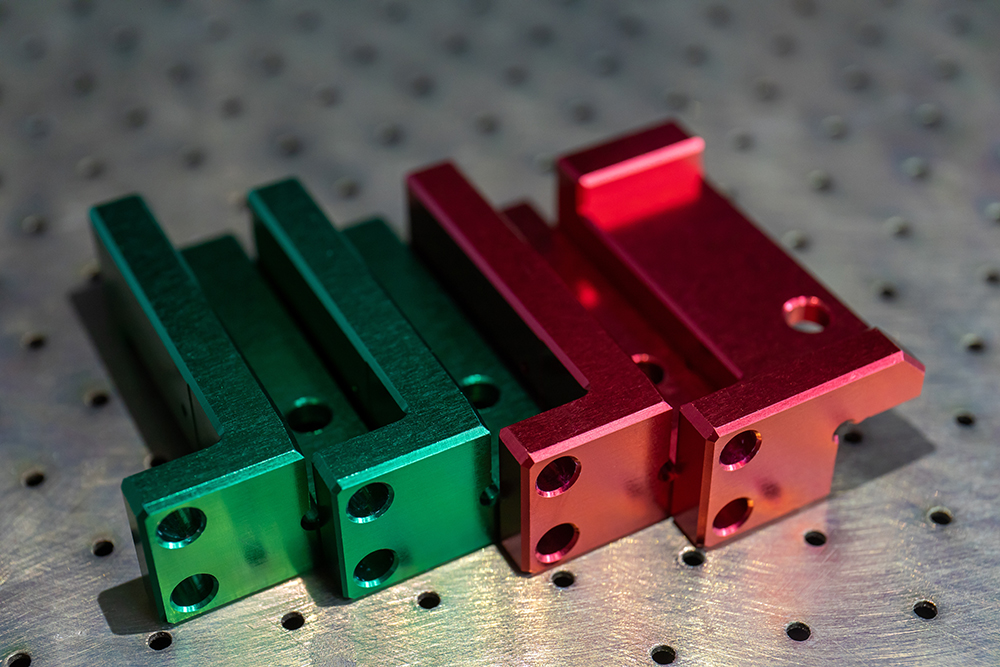
Why is aluminum alloy not suitable for electroplating?
The chemical properties of aluminum are relatively active. Suppose electroplating in the acidic electrolyte, the aluminum ions on the cathode will generate aluminum salts and hydrogen while obtaining electron reduction. In the case of an alkaline electrolyte, aluminum hydroxide and hydrogen are generated. Therefore, aluminum cannot be plated by electroplating. This is the same reason that the electrolysis of salt water does not obtain metallic sodium but instead accepts sodium hydroxide.
Finally, the die-cast aluminum alloy oxide surface does not work well.
Cast aluminum alloys and die castings generally contain high silicon content. The anodic oxide film is dark, and it is impossible to obtain a colourless and transparent oxide film—dark grey to black grey. Therefore, cast aluminum alloys are not suitable for anodizing.
However, the effect of anodizing treatment of zinc alloy die castings is particularly poor, the yield rate is meagre, and anodizing treatment is a very cumbersome process. Zinc alloy dies castings are usually surface treated by electroplating.